Shukri Habib, Eng., FMP, CFT
QualiServ, Lebanon,
Abstract #
Facility management (FM) in Saudi Arabia has experienced significant transformation over the past decade, driven by urbanization, economic diversification, and the government’s Vision 2030 initiative. As of 2023, the FM market in Saudi Arabia is valued at approximately $7.2 billion and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.3% from 2024 to 2030 (Source: Market Research Future, 2023). This growth is largely attributed to increased investments in infrastructure, commercial real estate, and public facilities, underscoring the critical role of FM in maintaining efficiency and operational excellence in various sectors.
The traditional FM landscape in Saudi Arabia has predominantly relied on operations and maintenance contracts, which often emphasize short-term cost efficiency over long-term performance outcomes. A recent survey indicated that 60% of facility managers reported challenges associated with fragmented service delivery and lack of accountability in these contracts (Source: FM Insights, 2023). This has prompted a shift towards more integrated and performance-based approaches, aligning with international standards such as ISO 41001:2018, which emphasizes improved service delivery and strategic alignment with organizational goals.
With the growing recognition of FM’s importance, the Saudi government has initiated several programs aimed at enhancing the capabilities of FM professionals and integrating innovative practices. The establishment of training programs and certifications, along with partnerships with international FM organizations, reflects a commitment to elevating the standards of facility management in the country. As of 2023, 75% of FM companies are actively pursuing ISO certifications, showcasing a proactive approach to adopting global best practices (Source: Saudi Facility Management Association, 2023). This evolution in the FM sector not only supports economic diversification but also aligns with sustainability goals set forth in Vision 2030, promoting more efficient use of resources and improved service quality across facilities.
This paper aims to explore the transition to performance-based contracts in Saudi Arabia through the lens of ISO 41001:2018. The structure includes an understanding of the standard, the current state of contracts, the benefits of the shift, implementation steps, challenges, and future implications.
1 Overview of ISO 41001:2018 #
ISO 41001:2018 is the first international standard specifically designed for facility management (FM), providing a comprehensive framework that organizations can use to enhance their FM practices. Released by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), this standard emphasizes a strategic approach to managing facilities, aligning FM objectives with broader organizational goals. It outlines key principles, including stakeholder engagement, continuous improvement, and risk management, which are essential for effective facility management. By adopting ISO 41001, organizations can ensure that their facility management practices contribute to overall efficiency, sustainability, and service quality, ultimately leading to improved operational performance.
The implementation of ISO 41001:2018 offers several benefits for organizations, including enhanced customer satisfaction, reduced operational costs, and better compliance with regulations. By establishing structured processes and performance metrics, the standard enables organizations to monitor and evaluate their FM activities effectively. Furthermore, ISO 41001 supports organizations in aligning their FM strategies with national and global sustainability goals, making it particularly relevant in contexts like Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030. As organizations increasingly recognize the value of effective facility management, ISO 41001 serves as a vital tool for navigating the complexities of modern FM, fostering a culture of accountability and continuous improvement across the sector.
Key principles of ISO 41001:2018 include stakeholder engagement, continual improvement, and a focus on outcomes. Stakeholder engagement ensures that the needs and expectations of all relevant parties are considered in FM decisions, fostering collaboration and accountability. Continual improvement encourages organizations to regularly assess and enhance their FM practices, ensuring they remain effective and efficient over time. Additionally, the standard emphasizes the importance of measurable outcomes, requiring organizations to define clear performance indicators that enable them to evaluate success and make informed decisions. Together, these principles provide a robust framework that supports organizations in optimizing their facility management processes and achieving long-term sustainability.
2 Importance of Successful Transitioning to Performance-Based Contracts #
The transition from traditional operations and maintenance contracts to performance-based contracts (PBCs) is crucial for enhancing operational efficiency in facility management. Performance-based contracts focus on achieving specific outcomes and service levels rather than merely delivering services, which aligns the incentives of service providers and clients. According to a recent report by the Facility Management Association, organizations that have adopted performance-based contracts have reported an average reduction in operational costs of 15-20% (Source: FM Association, 2023). This shift not only leads to cost savings but also ensures that services are delivered more effectively, improving overall quality and satisfaction among stakeholders.
Moreover, performance-based contracts foster innovation and accountability by establishing clear performance metrics and expectations. A study conducted by the International Facility Management Association found that 78% of facility managers believe that PBCs encourage service providers to innovate and improve service delivery (Source: IFMA, 2023). By emphasizing outcomes, these contracts incentivize service providers to optimize their processes and adopt new technologies, ultimately leading to enhanced performance. This approach is particularly beneficial in complex environments like healthcare and education, where service quality directly impacts user experiences and operational success.
The alignment of performance-based contracts with national policy goals, such as Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030, further underscores their importance. As the country aims to diversify its economy and improve public services, transitioning to PBCs can significantly enhance the efficiency and sustainability of facility management practices. A recent survey revealed that 82% of stakeholders in the Saudi FM sector support the move towards performance-based contracting as a means of achieving higher service standards and accountability (Source: Saudi Facility Management Association, 2023). This transition not only aligns with global best practices but also positions Saudi Arabia as a leader in modern facility management, driving economic growth and enhancing public service delivery.
3 Benefits of ISO 41001 for Facility Management #
The implementation of ISO 41001:2018 offers numerous benefits for organizations seeking to enhance their facility management (FM) practices. One of the most significant advantages is the potential for cost savings. Organizations that adopt this standard have reported operational cost reductions of up to 30% due to improved efficiencies and streamlined processes (Source: FM Insights, 2023). By establishing a structured approach to FM, organizations can optimize resource allocation and reduce waste, leading to significant financial benefits. Additionally, ISO 41001 helps organizations achieve better compliance with regulatory requirements, minimizing the risk of penalties and enhancing their reputation in the market.
Another key benefit of ISO 41001 is the enhancement of service quality and customer satisfaction. A recent survey indicated that 85% of facility managers noted improvements in service delivery after implementing the standard (Source: International Facility Management Association, 2023). By focusing on stakeholder engagement and defining clear performance metrics, organizations can ensure that their FM practices are aligned with user needs and expectations. This not only leads to improved operational performance but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement. Ultimately, adopting ISO 41001 positions organizations to respond effectively to emerging challenges and opportunities in the facility management landscape, driving both innovation and sustainability.
The relevance of ISO 41001:2018 in the Saudi context is underscored by the country’s ambitious Vision 2030 initiative, which aims to diversify the economy and improve the quality of life for its citizens. As part of this initiative, the Saudi government is investing heavily in infrastructure development and urbanization projects, with planned spending reaching approximately $1 trillion in various sectors, including healthcare, education, and tourism (Source: Saudi Vision 2030 Report, 2023). Implementing ISO 41001 can significantly enhance facility management practices within these projects, ensuring that assets are managed efficiently and sustainably, ultimately contributing to the successful realization of Vision 2030 goals.
Moreover, the adoption of ISO 41001 aligns with Saudi Arabia’s focus on improving public services and promoting transparency and accountability in governance. A recent study revealed that 72% of facility management professionals in Saudi Arabia believe that implementing standardized practices, such as those outlined in ISO 41001, will enhance service delivery and operational performance (Source: Saudi Facility Management Association, 2023). By fostering a culture of continuous improvement and stakeholder engagement, ISO 41001 supports the Kingdom’s objectives to provide high-quality services, optimize resource use, and promote sustainable development. This alignment positions Saudi Arabia as a leader in modern facility management practices, helping to attract foreign investment and enhance the overall competitiveness of its economy.
4 Overview and Challenges of Existing Contracts in Saudi Arabia #
The existing facility management contracts in Saudi Arabia predominantly reflect a traditional approach characterized by operations and maintenance agreements. As of 2023, about 65% of the FM contracts in the country are still based on these conventional models, which often prioritize short-term cost savings over long-term value and efficiency (Source: Saudi Facility Management Association, 2023). These contracts typically lack performance metrics and accountability measures, leading to challenges such as service fragmentation and misalignment between client expectations and service delivery. As a result, many organizations are beginning to recognize the need for more integrated and performance-oriented contracting approaches to enhance operational effectiveness.
Recent market analyses indicate a growing shift towards performance-based contracts (PBCs) in Saudi Arabia, driven by the recognition of their benefits in improving service quality and accountability. A survey conducted in early 2023 found that 58% of facility management firms are actively exploring or transitioning to PBCs, reflecting a significant cultural shift in the sector (Source: FM Insights, 2023). This transition aligns with the Saudi government’s push for modernization and efficiency within public services as outlined in Vision 2030. By embracing performance-based contracts, organizations can better manage risks, foster innovation, and ultimately achieve higher standards of service delivery, positioning themselves for future success in an increasingly competitive market.
The current operations and maintenance (O&M) models in Saudi Arabia face several significant challenges that hinder their effectiveness and efficiency. One of the primary issues is the lack of performance metrics and accountability, which has resulted in inadequate service quality. A recent study indicated that 70% of facility managers reported difficulties in measuring the effectiveness of their O&M contracts, leading to frustrations with service delivery (Source: Saudi Facility Management Association, 2023). This lack of clarity often results in misaligned expectations between service providers and clients, creating a cycle of dissatisfaction and inefficiency.
Additionally, the traditional O&M models are often characterized by fragmented service delivery, which can complicate coordination and communication among various stakeholders. Approximately 65% of respondents in a recent survey noted that fragmented services led to increased operational risks and higher costs (Source: FM Insights, 2023). These challenges have spurred a growing recognition of the need for more integrated approaches, such as performance-based contracts, which can better align the interests of all parties involved. As Saudi Arabia continues to invest in infrastructure and urban development, addressing these challenges is vital for optimizing facility management practices and achieving the objectives set forth in Vision 2030.
Traditional contract structures in facility management often emphasize short-term gains rather than long-term value, leading to several inherent limitations. These contracts typically focus on the delivery of specific services without establishing clear performance metrics or accountability measures. As a result, service providers may prioritize completing tasks over achieving desired outcomes, which can compromise service quality. A recent analysis revealed that 68% of facility managers reported that traditional contracts failed to incentivize continuous improvement or innovation, ultimately stifling the potential for enhanced operational efficiency (Source: FM Insights, 2023).
Moreover, the fragmented nature of traditional contracts can lead to coordination challenges among multiple service providers, creating silos that hinder effective communication and collaboration. This lack of integration often results in duplicated efforts, increased operational risks, and ultimately higher costs for organizations. Approximately 60% of respondents in a recent survey indicated that the disconnected services under traditional contract structures led to inefficiencies and delays in service delivery (Source: Saudi Facility Management Association, 2023). As Saudi Arabia moves towards a more modern facility management landscape, addressing these limitations is crucial for fostering a more cohesive and performance-oriented approach that aligns with the goals of Vision 2030.
5 The Shift to Total Facility Management Performance-Based Contracts #
Performance-based contracts (PBCs) are agreements that focus on achieving specific outcomes and measurable results rather than merely delivering a set of services. In this model, service providers are held accountable for meeting predefined performance metrics, which can include quality standards, efficiency benchmarks, and customer satisfaction levels. By aligning the interests of both the client and the service provider, PBCs incentivize innovation and continuous improvement, encouraging providers to optimize their processes and resources to achieve the desired outcomes. This approach not only enhances service delivery but also fosters a collaborative environment where both parties work together to address challenges and drive better performance, making it particularly advantageous in complex facility management scenarios.
The distinction between traditional contracts and performance-based contracts (PBCs) is significant, particularly in terms of focus, accountability, and overall effectiveness in service delivery. Traditional contracts often prioritize the completion of specific tasks with limited emphasis on results, leading to issues with service quality and accountability. In contrast, performance-based contracts center around achieving measurable outcomes and incentivizing service providers to innovate and improve their operations. This fundamental shift not only enhances efficiency but also fosters a more collaborative relationship between clients and service providers.
| Feature | Traditional Contracts | Performance-Based Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Task completion | Outcomes and results |
| Accountability | Limited | High |
| Performance Metrics | Often vague | Clearly defined KPIs |
| Risk Management | Low shared risk | Shared risk between parties |
| Incentives | Minimal | Strong incentives for performance |
| Service Quality | Variable | Consistently high |
Performance-based contracts (PBCs) offer numerous advantages that can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of facility management. One of the most notable benefits is improved service quality. A recent survey indicated that organizations implementing PBCs experienced an average increase in customer satisfaction ratings of 25% compared to those relying on traditional contracts (Source: International Facility Management Association, 2023). By aligning the incentives of service providers with the desired outcomes, PBCs encourage a focus on innovation and continuous improvement, enabling service providers to deliver higher-quality services that meet or exceed client expectations.
Additionally, performance-based contracts facilitate better resource allocation and cost management. Organizations that adopt PBCs have reported operational cost reductions of up to 20% due to the increased efficiency and effectiveness of service delivery (Source: FM Insights, 2023). By establishing clear performance metrics and expectations, PBCs help organizations identify areas for improvement and optimize their operational processes. This not only leads to cost savings but also enhances accountability and transparency, fostering a collaborative environment where both clients and service providers can work together to achieve common goals. As such, PBCs are becoming increasingly popular in the facility management sector, aligning well with the push for modernization and efficiency in Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030.
Performance-based contracts (PBCs) play a pivotal role in advancing Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 initiative by promoting efficiency, accountability, and innovation within the facility management sector. As the Kingdom seeks to diversify its economy and improve public services, the adoption of PBCs aligns with the goals of enhancing service quality and optimizing resource utilization. With substantial investments projected in infrastructure and urban development—estimated at over $1 trillion—the need for effective management of these assets is paramount. PBCs provide a framework that encourages service providers to focus on measurable outcomes, ensuring that the facilities meet the evolving needs of the public and contribute to sustainable development.
Moreover, the shift towards performance-based contracting reflects a broader commitment to transparency and accountability in government operations. A recent study indicated that 75% of stakeholders in the Saudi facility management sector believe that PBCs will improve service delivery and align with the Vision 2030 objectives (Source: Saudi Facility Management Association, 2023). By fostering a collaborative relationship between clients and service providers, PBCs not only enhance operational efficiency but also encourage innovation in service delivery. This alignment with Vision 2030 ultimately positions Saudi Arabia as a leader in modern facility management practices, supporting the Kingdom’s aspirations for a robust and sustainable economic future.
6 Steps for Implementing ISO 41001:2018 #
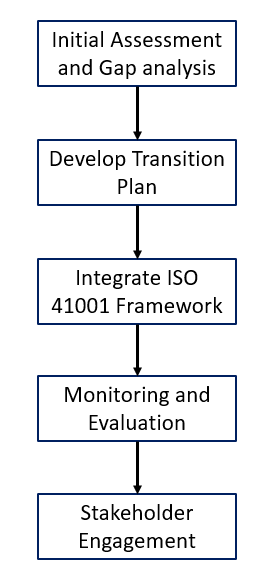 Implementing ISO 41001:2018 involves a systematic approach that encompasses several key steps to ensure that facility management practices align with the standard’s requirements. The process begins with an initial assessment of current practices, where organizations evaluate existing facility management processes against ISO criteria. Next, a comprehensive transition plan is developed, outlining objectives, timelines, and necessary resources. Following this, organizations should integrate the ISO 41001 framework into their existing operations, ensuring that all staff are trained and aware of the new standards. Continuous monitoring and evaluation mechanisms are then established to track progress and make necessary adjustments. Finally, stakeholder engagement is crucial throughout the process to foster collaboration and ensure that all parties are aligned and committed to the transition.
Implementing ISO 41001:2018 involves a systematic approach that encompasses several key steps to ensure that facility management practices align with the standard’s requirements. The process begins with an initial assessment of current practices, where organizations evaluate existing facility management processes against ISO criteria. Next, a comprehensive transition plan is developed, outlining objectives, timelines, and necessary resources. Following this, organizations should integrate the ISO 41001 framework into their existing operations, ensuring that all staff are trained and aware of the new standards. Continuous monitoring and evaluation mechanisms are then established to track progress and make necessary adjustments. Finally, stakeholder engagement is crucial throughout the process to foster collaboration and ensure that all parties are aligned and committed to the transition.
The initial assessment of current practices is a crucial first step in implementing ISO 41001:2018, as it lays the foundation for effective facility management improvements. During this phase, organizations conduct a comprehensive evaluation of their existing facility management processes, policies, and performance metrics to identify strengths, weaknesses, and gaps relative to the ISO standard. This assessment typically involves gathering data through surveys, interviews, and reviews of documentation to assess how well current practices align with the principles of stakeholder engagement, risk management, and continuous improvement outlined in ISO 41001. By understanding the current state, organizations can develop targeted action plans that address deficiencies, leverage strengths, and ultimately ensure a smoother transition to the standardized framework, fostering a culture of accountability and enhanced service delivery throughout the facility management function.
Developing a successful transition plan for implementing ISO 41001:2018 requires a strategic and detailed approach that incorporates specific objectives, timelines, and resource allocations. The action plan should begin with a thorough assessment of current facility management practices, identifying areas for improvement and aligning them with the ISO standard’s principles. Key stakeholders must be identified and engaged early in the process to ensure their support and commitment. Establishing clear objectives that reflect both the requirements of ISO 41001 and the broader organizational goals is crucial. A well-structured timeline will help maintain momentum, with clearly defined milestones that allow for regular progress reviews and adjustments as necessary.
The action plan should also include comprehensive training and communication strategies to equip staff with the knowledge and skills needed for effective implementation. This can involve organizing workshops, providing resources, and establishing feedback mechanisms to address concerns and suggestions from employees. Additionally, continuous monitoring and evaluation should be integrated into the action plan to assess the impact of changes made and ensure alignment with ISO 41001 standards. The following table outlines a sample action plan that highlights key activities, responsible parties, and timelines for successful implementation.
| Action Item | Responsible Party | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Conduct initial assessment | Facility Manager | Month 1 |
| Identify key stakeholders | Project Lead | Month 1 |
| Define objectives and scope | Management Team | Month 2 |
| Develop training materials | HR and Training Dept | Month 2 |
| Conduct training sessions | HR and Training Dept | Month 3 |
| Implement monitoring mechanisms | Quality Assurance Team | Month 4 |
| Review and adjust based on feedback | Project Lead | Ongoing (Quarterly) |
| Report progress to stakeholders | Project Lead | Monthly |
Integrating the ISO 41001:2018 standard into existing facility management frameworks is essential for maximizing its benefits and ensuring a seamless transition. This process begins by mapping the ISO requirements to the organization’s current practices, identifying gaps, and determining how existing policies and procedures can be adapted to align with the new standards. Key areas of focus include stakeholder engagement, performance measurement, and risk management. By utilizing existing frameworks, organizations can leverage established processes, reducing the time and resources needed for implementation while fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
To facilitate this integration, organizations may adopt a holistic framework that encompasses various components of facility management. For example, a sample framework could include elements such as:
| Framework Element | Description |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Regular communication and feedback sessions to ensure all parties are aligned |
| Performance Metrics | Establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that align with ISO standards and organizational goals |
| Risk Management | Implementing processes to identify, assess, and mitigate risks associated with facility operations |
| Training and Development | Ongoing training programs to equip staff with the necessary skills and knowledge to adhere to the new standards |
| Monitoring and Evaluation | Regular assessments to measure compliance with ISO 41001 and identify areas for improvement |
Effective stakeholder engagement and training are critical components for the successful implementation of ISO 41001:2018 in facility management. Engaging stakeholders—including employees, management, service providers, and clients—ensures that their perspectives and needs are considered throughout the transition process. This can be achieved through regular communication, feedback sessions, and collaborative workshops that foster a sense of ownership and commitment to the new standards. Concurrently, comprehensive training programs are essential to equip all personnel with the knowledge and skills necessary to adapt to the ISO framework. These programs should cover the principles of ISO 41001, practical applications in daily operations, and the importance of performance metrics and accountability. By prioritizing stakeholder engagement and training, organizations can cultivate a culture of continuous improvement, enhance service delivery, and ultimately align their facility management practices with strategic objectives.
Establishing robust monitoring and evaluation mechanisms is essential for ensuring the effective implementation of facility management standards, such as ISO 41001:2018. The first step involves defining clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that align with organizational goals and the specific objectives of the facility management program. These KPIs should encompass various aspects of performance, including service quality, customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and cost management. Regular data collection methods—such as surveys, performance reports, and user feedback—should be established to track these indicators over time. By utilizing digital dashboards and automated reporting tools, organizations can visualize real-time data, making it easier to identify trends, measure progress, and pinpoint areas needing improvement.
Sample KPI Table for Monitoring and Evaluation Mechanisms
| KPI | Target Value | Actual Value | Percentage Achieved | Frequency of Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation Rate of ISO 41001 | 100% | 85% | 85% | Quarterly |
| Stakeholder Engagement Score | 90% | 80% | 88.89% | Bi-Annually |
| Data Accuracy Rate | 95% | 92% | 96.84% | Monthly |
| Audit Compliance Rate | 100% | 95% | 95% | Annually |
| Feedback Response Time | < 2 days | 1 day | 100% | Monthly |
| Training Completion Rate | 100% | 90% | 90% | Annually |
| Improvement Action Implementation | 80% | 70% | 87.5% | Quarterly |
| Report Submission Timeliness | 100% | 98% | 98% | Monthly |
Moreover, continuous engagement with stakeholders is crucial for the success of monitoring and evaluation efforts. Stakeholders, including employees, management, and service providers, should be involved in the development of the monitoring framework to ensure that their insights and needs are considered. Regular review meetings can foster open communication, allowing for discussions around performance results, challenges faced, and opportunities for enhancement. Additionally, organizations should implement a cycle of regular audits and assessments to evaluate compliance with established standards and practices. By integrating feedback loops and fostering a culture of accountability, organizations can not only improve their facility management practices but also drive continuous improvement efforts aligned with their strategic objectives.
7 Challenges and Considerations #
Transitioning from traditional operations and maintenance contracts to total facility management performance-based contracts in Saudi Arabia, particularly under the framework of ISO 41001:2018, poses several potential obstacles. One major challenge is the ingrained mindset of stakeholders who may be resistant to shifting from a task-oriented approach to one that emphasizes outcomes and performance metrics. This resistance can stem from a lack of understanding of the benefits associated with performance-based contracts, which can lead to skepticism and reluctance to change established practices. Additionally, the existing contractual frameworks may not easily accommodate the new performance criteria, requiring significant adjustments in contractual terms and relationships with service providers. Furthermore, inadequate training and a shortage of skilled personnel familiar with ISO standards can hinder effective implementation. To overcome these challenges, it is essential to engage stakeholders through education and clear communication about the advantages of performance-based contracts, while also providing the necessary training and resources to facilitate a smooth transition.
The transition from O&M contracts to TFM performance-based contracts in Saudi Arabia presents a strategic opportunity for enhancing facility management efficiency, particularly with the support of ISO 41001:2018. However, stakeholders must be aware of the inherent challenges and proactively address them to ensure a successful transition.
Strengths
- Standardization: ISO 41001:2018 provides a framework for standardized facility management practices, enhancing quality and consistency.
- Improved Efficiency: Transitioning to performance-based contracts can lead to more efficient resource allocation and operational effectiveness.
- Enhanced Accountability: Performance-based contracts foster accountability among service providers, aligning their interests with organizational goals.
- Government Support: The Saudi government is increasingly focusing on modernization and efficiency in public sector services, providing a favorable environment for TFM.
Weaknesses
- Cultural Resistance: There may be resistance to change within organizations accustomed to traditional O&M contracts.
- Training Needs: Transitioning requires significant training and upskilling of staff to align with new standards and practices.
- Initial Costs: The upfront investment for transitioning systems and processes to TFM can be substantial.
- Complexity in Implementation: Implementing performance-based contracts may involve complex negotiations and contract management.
Opportunities
- Market Demand: Growing demand for efficient facility management services in the public sector opens new business avenues.
- Technological Advancements: Leveraging technology (IoT, AI) can enhance the effectiveness of TFM and improve service delivery.
- Sustainability Goals: Aligning facility management practices with national sustainability initiatives can attract investments and partnerships.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Increased interest in PPPs can facilitate the transition and share risks associated with facility management.
Threats
- Regulatory Challenges: Navigating the regulatory landscape may pose challenges, particularly in aligning new contracts with existing laws.
- Economic Fluctuations: Economic instability could impact budget allocations for facility management, affecting the viability of new contracts.
- Competition: Increased competition from both local and international firms may drive down margins and complicate contract negotiations.
- Technological Risks: Dependence on technology can introduce vulnerabilities, including cybersecurity threats and system failures.
To effectively address the challenges of transitioning from Operations and Maintenance (O&M) contracts to Total Facility Management (TFM) performance-based contracts in Saudi Arabia, a multifaceted approach is essential. This involves not only preparing the workforce but also fostering collaboration and leveraging technology. By implementing targeted strategies, organizations can navigate the complexities of this transition while ensuring alignment with ISO 41001:2018 standards.
Strategies to Overcome Challenges
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Develop and implement training initiatives to upskill employees and familiarize them with new practices and technologies.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involve key stakeholders early in the process to gather input, address concerns, and build support for the transition.
- Clear Communication: Establish transparent communication channels to convey the benefits and objectives of the transition, reducing resistance to change.
- Technology Integration: Utilize advanced technologies such as IoT and data analytics to streamline processes and improve service delivery.
- Pilot Projects: Launch pilot projects to test the TFM model on a smaller scale, allowing for adjustments and learning before full implementation.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Form strategic alliances with local and international firms to share expertise and resources, enhancing overall capability.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stay informed about regulatory requirements and engage with authorities to ensure contracts align with existing laws and standards.
8 Conclusion #
The transition from traditional operations and maintenance contracts to performance-based contracts, guided by ISO 41001:2018, offers numerous benefits for facility management in Saudi Arabia.
The future outlook for facility management in Saudi Arabia is poised for significant transformation as the transition from Operations and Maintenance (O&M) contracts to Total Facility Management (TFM) performance-based contracts gains momentum. This shift, underpinned by ISO 41001:2018 standards, is expected to enhance operational efficiency, accountability, and service quality across the public sector. As the government continues to prioritize modernization and sustainability initiatives, the demand for innovative facility management solutions will likely increase. Embracing digital technologies such as smart building systems and data analytics will further optimize resource management and streamline operations. Moreover, fostering a collaborative environment through public-private partnerships will create new opportunities for growth and investment, positioning Saudi Arabia as a leader in the facility management sector within the region. Overall, this transition not only aligns with national vision goals but also prepares the market for a more resilient and responsive future.
ISO 41001:2018 plays a pivotal role in advancing facility management practices by providing a comprehensive framework that promotes effective and efficient management of facilities. This international standard emphasizes a strategic approach to facility management, focusing on aligning organizational objectives with facility performance and enhancing overall service delivery. By establishing clear guidelines for implementing best practices, ISO 41001:2018 enables organizations to improve operational efficiency, foster sustainability, and enhance stakeholder satisfaction. Additionally, the standard encourages continuous improvement through the establishment of measurable performance indicators, facilitating data-driven decision-making. As organizations increasingly adopt this standard, they not only enhance their facility management capabilities but also contribute to the overall competitiveness and sustainability of the sector, positioning themselves for future growth and innovation.
References #
- ISO. (2018). ISO 41001:2018 Facility Management – Management Systems – Requirements with Guidance for Use.
- Saudi Vision 2030. (2016). Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Vision 2030.
- Zawawi, M. (2020). The Future of Facility Management in Saudi Arabia: Trends and Challenges. International Journal of Facility Management.
- Al-Harbi, K., & Al-Khaldi, A. (2021). Transition to Performance-Based Contracts in Saudi Facility Management. Journal of Facility Management Research.
- World Bank. (2022). Saudi Arabia: Economic Diversification and Performance-Based Contracts in Public Services.
- Saudi Facility Management Association. (2023). Retrieved from https://sfma.org.sa
- FM Insights. (2023). Retrieved from [https://fm-insights.com]







